At a time when countries around the world are looking to reduce their climate impacts by moving away from the use of fossil fuels in their energy systems and seeking to make their economies more resilient to climate impacts, it is vital to re-examine fossil fuel subsidies across their many forms and uses.
The combustion of fossil fuels is the major anthropogenic contributor to climate change. Fossil fuel subsidies encourage the consumption and production of fossil fuels, increasing climate change and local pollution and making the continued development and use of fossil fuels more attractive against alternatives such as renewable energy.
With reference to how fossil fuels are produced, traded, and consumed, this policy paper identifies which are the largest and most harmful categories of fossil fuel subsidies globally, what are their aims and objectives, and how they can be better targeted. Based on this analysis, the paper recommends categories of fossil fuel subsidies that should be prioritized for reform. The paper concludes by reviewing progress and lessons on fossil fuel subsidy reform, the rationale for collective action, and how such collective action could be taken forward at the WTO in collaboration with other organizations and processes.
Collective action is an important way to drive fossil fuel subsidy reform and the World Trade Organization has a critical role to play to support this reform.
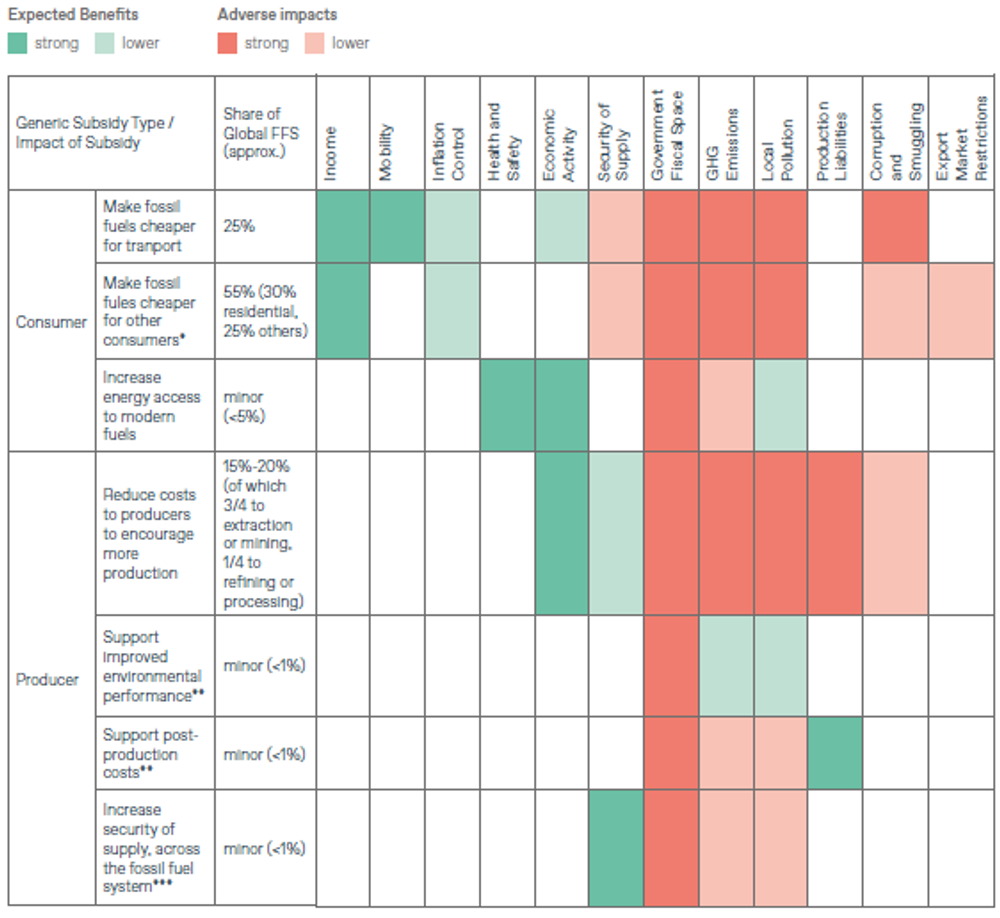
Expected Benefits and Adverse Impacts of Fossil Fuel Subsidies and Approximate Share of Global Fossil Fuel Subsidies
Recommended citation: Wooders, P. (2024). Fossil fuel subsidy reform: Options for inclusive collective action at the World Trade Organization. Forum on Trade, Environment, & the SDGs (TESS).
TESS at the World Trade Organization
This work is part of our initiative supporting inclusive cooperation
on trade, environment, and sustainable development at the WTO.





